Lagos, Nigeria’s bustling megacity and one of the fastest-growing urban areas in the world, is facing an escalating challenge: flooding. As rising sea levels and unpredictable rainfall patterns intensify, the city’s infrastructure is under significant strain, threatening the lives, livelihoods, and economic stability of its millions of residents. In response to this urgent crisis, innovative solutions are emerging in the form of flood-resilient infrastructure designed to mitigate the devastating impacts of severe weather events. This article examines the transformative strategies being implemented in Lagos, highlighting how urban planning, engineering advancements, and community engagement are converging to create a safer, more sustainable city. As Lagos navigates the complexities of climate change, it stands at the forefront of a critical movement towards resilience, offering valuable lessons for other flood-prone cities around the globe.
Table of Contents
- Innovative Approaches to Flood-Resilient Urban Planning in Lagos
- Investing in Sustainable Drainage Systems to Mitigate Flood Risks
- Community Engagement and Stakeholder Collaboration in Flood Resilience
- Policy Frameworks and funding strategies for Transforming Lagos Infrastructure
- Insights and Conclusions
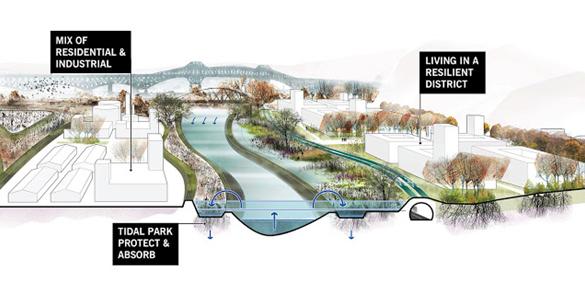
Innovative Approaches to Flood-Resilient Urban planning in Lagos
the city of Lagos is embracing transformative strategies aimed at enhancing its flood resilience, acknowledging that urban planning must evolve in the face of climate change challenges. Key initiatives include:
- Green Infrastructure: Incorporating parks, green roofs, and permeable pavements to absorb rainwater and reduce surface runoff.
- Wetland Restoration: Revitalizing mangroves and natural wetlands which act as buffers against flooding, improving water quality, and providing habitats for various species.
- Smart Drainage Systems: Implementing advanced drainage solutions equipped with sensors to monitor water levels and predict flooding events in real time.
Additionally, collaboration between government agencies, NGOs, and local communities is crucial for accomplished implementation. A recent study highlighted various sustainable urban planning techniques, summarized in the table below:
| Technique | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Rainwater Harvesting | Collecting and storing rainwater for reuse. | Reduces demand on water supply and mitigates flooding. |
| Flood-Resilient Housing | Designing homes to withstand water damage. | Enhances safety and reduces economic loss. |
| Urban Reforestation | Planting trees in urban areas to increase absorption. | improves air quality and supports biodiversity. |
Investing in Sustainable Drainage Systems to Mitigate Flood Risks
As Lagos grapples with increasing flood risks exacerbated by climate change and urbanization, investing in sustainable drainage systems (SuDS) emerges as a crucial strategy. These systems aim to mimic natural drainage processes, reducing surface water runoff and improving water quality. Adopting SuDS can significantly mitigate flooding by improving water absorption in urban settings, especially in densely populated areas where traditional drainage approaches frequently enough fail. The implementation of permeable pavements, green roofs, and bioswales not only enhances aesthetic values but also promotes a healthier ecosystem by supporting biodiversity and enhancing urban resilience.
Municipal authorities and urban planners are encouraged to prioritize the integration of these innovative drainage solutions into their infrastructure development plans. A comprehensive approach may include:
- Community Engagement: Involving local communities in the design and maintenance of SuDS to ensure they meet specific needs.
- Funding Mechanisms: Establishing dedicated funds or incentives for projects that showcase sustainable drainage techniques.
- Regulatory Support: Creating and enforcing policies that mandate SuDS in new developments and major renovations.
To further analyze the impact of SuDS, the table below highlights key benefits:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Flood Reduction | Contributes to managing stormwater and reduces the likelihood of urban flooding. |
| Water Quality Advancement | Filters pollutants and improves the quality of runoff before it reaches water bodies. |
| Enhanced Green Spaces | Incorporates vegetation and landscaping, increasing urban greenery. |
| Cost Efficiency | Reduces long-term infrastructure maintenance costs by preventing drainage system failures. |
Community Engagement and Stakeholder collaboration in Flood Resilience
Community engagement and collaboration with stakeholders are crucial for the successful implementation of flood resilience initiatives in lagos. By fostering inclusive dialogue among residents, local governments, and non-governmental organizations, stakeholders can ensure that the infrastructure developed effectively addresses the unique challenges posed by flooding. Such collaborations provide avenues for valuable input from those who are most affected by flooding, leading to more tailored solutions that can enhance overall community resilience. Strategies to engage the community may include:
- Public Workshops: Offering platforms for residents to voice their concerns and suggestions.
- Feedback Loops: Establishing ongoing channels for community feedback throughout the project lifecycle.
- Collaboration with Local Leaders: Partnering with trusted community figures to better reach diverse segments of the population.
Moreover, partnerships with private sector actors can also aid in the development and financing of resilient infrastructure. These collaborations can provide essential resources and expertise that may otherwise be unavailable. Identifying common goals among stakeholders can lead to innovative approaches to financing, designing, and implementing flood resilience projects. A structured collaboration framework could include:
| Stakeholder Type | Role | Contribution |
|---|---|---|
| Community Residents | Feedback Providers | Local knowledge and lived experiences |
| Local Government | Policy Makers | Regulatory support and funding |
| Non-Governmental Organizations | Facilitators | Expertise and outreach capabilities |
| Private Sector | Investors | Technical solutions and financial backing |
Policy Frameworks and Funding Strategies for Transforming Lagos infrastructure
To catalyze the transformation of Lagos’ infrastructure into a flood-resilient model, a robust policy framework is essential. This framework should prioritize the integration of sustainable urban development practices while addressing the immediate challenges posed by climate change. Some key policies to consider include:
- Comprehensive Urban Planning: Enforce zoning regulations that promote resilience and flood mitigation within high-risk areas.
- Investment in Green infrastructure: Prioritize the development of parks, green roofs, and permeable pavements to facilitate effective water absorption.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Foster collaborations with private entities to leverage innovation and investment in infrastructure development.
- community Engagement: Involve local communities in planning processes to ensure openness and sustainability.
Funding strategies will play a crucial role in realizing these policies. A multi-faceted approach to financing can unlock resources needed for these transformative projects. Potential funding avenues include:
- International Grants: Seek funding from global climate initiatives aimed at urban resilience.
- Government Bonds: Issue infrastructure bonds specifically earmarked for flood-resilient projects.
- Corporate Sponsorships: Attract investments from corporations committed to sustainability.
| Funding Source | Amount (Estimated) | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| International Climate Funds | $200 million | Support sustainable projects |
| Government Infrastructure Bonds | $150 million | Finance flood resilience |
| Corporate Sponsorships | $100 million | Invest in innovation |
Insights and Conclusions
As Lagos confronts the dual challenges of rapid urbanization and climate change, the rise of flood-resilient infrastructure represents a pivotal shift in the city’s approach to development and urban planning. This transformation, fueled by innovative engineering, sustainable practices, and community engagement, is more than just a response to environmental threats; it is a proactive strategy aimed at safeguarding the future of one of Africa’s most vibrant metropolises. By integrating advanced drainage systems,green roofs,and permeable surfaces into the urban fabric,Lagos is setting a precedent for resilience that can inspire other cities facing similar challenges.
Lagos is not merely adapting to its environmental realities; it is indeed redefining them. The commitment to creating a flood-resilient city enhances public safety, boosts economic viability, and fosters a sustainable urban environment. As investments in infrastructure continue to grow and collaborative efforts expand, Lagos stands poised to emerge as a model of resilience in the face of adversity, offering valuable lessons for cities around the globe. The journey towards a more flood-resilient Lagos has begun, and the outcomes promise to be transformative not just for the city, but for the millions of residents who call it home.